Ans: The SaaS sales definition is to sell cloud-based software products to businesses. This is a majorly subscription-based model that offers real business solutions.
SaaS Sales Process: Everything You Must Know in 2025
With the world completely gravitating towards digitalization, SaaS is the fastest-growing industry today. Even traditional brands and businesses have made a big leap to switch to a cloud-based subscription model. However, the truth is that selling Software-as-a-Service is much harder and takes a totally different approach than selling physical products.
So, how to crack it? Well, SaaS sales can be done by nurturing leads and providing an excellent customer journey. As one must know the complete cycle, SaaS for sale funnels, we have explained everything from scratch in this blog.
What is SaaS Sales?

SaaS Software Sales simply implies selling cloud-based software or applications to a customer. It can be done via a one-time payment and purchase model or a subscription-based model. The customer has to pay for the software you offer, and they get full access to the features.
Software as a service demands regular updates, audits, and a strong customer support team to provide solutions to existing and potential customers. Unlike the traditional sale, the SaaS sales team has to finalize the product, onboard the customers, train, and even up-scale.
Sounds pretty tough, right? However, the entire sales SaaS cycle can be completed pretty smoothly if you follow a streamlined method. Let’s understand it deeply in the next section.
SaaS Sales Funnels

According to the experts, the whole B2B SaaS industry runs on the basis of the funnels, which can be broadly determined as the key stages.
Stage 1: Awareness
In this stage, the potential customers find the product via avenues such as SEO, paid advertisements, social platforms, or recommendations. The goal in this case is to capture interest and enhance brand recognition.
Since there are already many brands existing in the same niche, it becomes important to catch the eyes of the customers multiple times.
Stage 2: Interest
Once you have created awareness of the business and the potential customers show interest in your work, they will visit your website, sign up for free trials, attend the free sessions, and even look through the resources. These are the lead magnets that can get converted if your product is worth it.
Stage 3: Evaluation
Now, generally, the potential customers compare your products and offerings to your competitors. They will look for testimonials, examine costs, and might ask for a demonstration. The SaaS sales training team might help to address inquiries and showcase benefits.
Stage 4: Purchase
After this, the leads convert into paying clients. During the onboarding process, the SaaS sales training team needs to demonstrate the product, provide pricing transparency, and provide proper sales support to close the final deal.
Stage 5: Retention
It doesn’t stop after closing the deal; the companies need to focus on retaining the customers. The SaaS sales representative has to constantly check in with clients, update them on changes, and provide support when needed. This builds trust and gains the loyalty of the customer.
Stage 6: Expansion
In this stage, the happy customers may turn into devoted users, endorsing the product or opting for premium subscriptions. This phase allows upselling or cross-selling new products to the clients.
The SaaS sales cycle is not at all a linear path and requires attention and care towards the customers, but these things can very well translate into great success!
Check Out: Top ERP System Examples: Best Business Management Tools You Must Know About
SaaS Software Sales Metrics
SaS sales can be measured via many metrics; however, to sustain and focus on the goals, here are the most essential metrics you must learn about:
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
The revenue is the ultimate goal to achieve, and MRR helps to predict that. This metric explains how much the company is receiving from the paying customers each month and how fast it is growing.
| MRR = Total Number of Paying Customers × Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA) |
Let’s say, Linda Tech currently has 500 onboarded clients paying $50 each.
Its monthly recurring revenue will be: 500 X $50 = $25,000
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
Similar to MRR, ARR gives yearly projections. It checks the books of the entire year and predicts the year-end revenue and growth rate of the firm.
| ARR = MRR × 12 |
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
This is a metric that explains how much is spent on acquiring a single customer. It is important to make marketing budgets and strategies. If the CAC is high and the returns are low, this means the company must re-evaluate its marketing rules.
| CAC = Total Sales and Marketing Amount / Number of New Customers Acquired |
Customer Lifetime Value
This metric explains the overall income you anticipate from a client throughout their whole association with your business. A large CLTV relative to CAC indicates a viable business model.
| Customer Lifetime Value = Average Revenue Per Account x Gross Margin x Average Customer Lifespan |
Churn Rate
This metric is the most crucial one to learn, as it determines the number of people who have canceled your subscription or do not renew the plan. The lower the churn rate, it means the product and customer fit is, and the customer is satisfied with the service.
| Churn Rate = (Customers Lost During Period / Total Customers at Start of Period) × 100 |
Explore the SaaS Sales Process
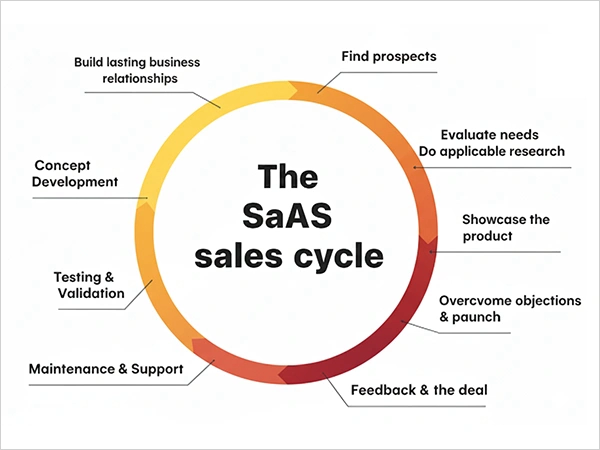
The SaaS sales process is more of a manual process that the company has to follow to turn prospects into paying customers. This cycle majorly focuses on consultation and building a long-term relationship with the customer.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the SaaS sales process:
- Prospecting: The first step is finding and identifying prospects. This includes extensive market research using targeted tools and data analytics. You can use multiple marketing and outreach methods like email campaigns, social selling, or inbound marketing.
- Lead Generation: The sales team then uses industry frameworks called BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline) and CHAMP (Challenges, Authority, Money, Prioritization) to determine the quality of the leads.
- Discovery Call: The sales representative gets on a call with the customer. This discovery call helps to understand the needs, challenges of the customers. It allows providing value-driven solutions and real case studies to influence the customer.
- Product Demo: The sales rep personalizes the product demo for each client to address their pain points, highlights the solutions, and explains how it can help them in the long run.
- Proposal and Negotiation: At this stage, the potential client and sales rep talk about the subscription fees, service level agreements, features, and transparency. There are high chances that negotiations may revolve around the price structures of cancellation terms.
- Closing Deal: When the client agrees fully, the deal is successfully closed. Following it comes internal approvals, signing contracts, and coordinating with legal bodies to authenticate everything.
Step-By-Step Approach to Sell SaaS
Selling software as a service requires lots of determination and a consultative approach. Here, you are not selling a product, but a solution that a customer needs and is willing to buy. The biggest gap arises when you do not know your product, and the customer does not understand the pain points, but it’s all a game of patience and a strategic approach.
Here are a few steps that will help you sell SaaS effectively:
- Know the Pulsing of Your Product: Before just selling your product, you need to think of it as a solution for the people and the market. Understand how your software fits with the needs, what value it can provide, its pricing, target audience, and more. Here are a few points to get started:
- Problems it solves
- The benefits people can get
- The USP
- How is it better than other solutions?
- Determine Your Ideal Customer: Not every model suits everyone, and trying to capture the whole market can drain your reach. Your ideal customer can be determined by:
- Industry type
- Business type
- Budget of the customer
- The company sizes you are targeting
This narrow approach can help you gain quality leads over time.
- Find and Qualify Leads: You must use tools like LinkedIn, Apollo, Zoom Info, and CRM tools to find potential clients. When finding the right lead:
- See if you can help them.
- What problems are they facing?
- Does your product align with their business?
- Are they using any existing product, and what are the flaws?
- Prepare a Proper Pitch: A Generic sales pitch won’t help you convert clients. You must analyze each potential customer and craft a well-documented pitch targeting them. Tailor your outreach with proper call-to-actions, contact details, the features, offerings, and real-case studies.
- Offer Free Demos: This step is necessary for initial loyalty-gaining purposes. Let the client test the product, and you focus on storytelling and giving real-use cases of other clients.
- Handle Rejections and Follow-Up: Not every lead will be converted, so you must stay patient and keep doing the job by searching for new potential leads. If any lead asks for follow-up, make sure to check in with them within 7-14-30 day period.
By following the above steps, you can successfully complete the SaaS sales cycle.
What are the Career Options in SaaS?
The SaaS industry is growing and has a high demand for multiple job profiles. Whether you want to pivot into the SaaS industry or are just starting a fresh career, roles like sales, marketing, customer success, and product management can have a very high scope.
These are the core skills needed for a successful SaaS career:
- Tech Knowledge: You must know how SaaS products work. A good understanding of APIs, dashboards, operations, and cloud platforms is needed.
- Analytical Thinking: Most software products run on data; thus, you must have an idea of how to gather data to measure success, loopholes, and optimize workflows.
- Customer-Focused Approach: No matter whether you are in sales or backend, addressing customer issues is fundamental.
- Communication is the Key: You must know how to do clear verbal communication to convert the clients and provide support.
Wrapping Up!
SaaS sales are not about selling a traditional product to a customer; it’s all about providing real value and a genuine solution. As a large percentage of the economy is shifting towards cloud-based platforms, more and more problems are arising, and this is your opportunity to offer the best solutions.
With the SaaS sales meaning, funnels, sales cycle, and step-by-step client closing and consultative approach given in this blog, we hope you will achieve great heights and scale your company’s revenue.
Read Next: ERP vs CRM: Understand the Key Differences, Functions, Benefits, and More
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What Is A SaaS Sales?
Q: Does SaaS Sales Pay Well?
Ans: Yes, the SaaS sales job generally offers high base salaries, performance bonuses, and commissions on closed deals.
Q: Is Selling SaaS Difficult?
Ans: Selling SaaS is tough as it requires tech knowledge, analytical thinking, and relationship-building skills. However, after studying the product inside out and the target audience, the journey gets easier.
Q: Can You Make A Lot Of Money In SaaS Sales?
Ans: Yes, top SaaS sales performers can earn a six-figure income through commissions, freelancing, base salary, and other incentives.
Q: Do You Need A Degree For SaaS Sales?
Ans: It is not mandatory to have a degree, but skill sets like communication, product knowledge, and sales experience are required. Build a solid portfolio to work with big companies.
Sources